Ports and Connectors are divided into three types,
they are as follows:
1) Legacy Multifunction Port (L.M.P):
a)
Serial Ports:
9-Pin Serial Port:
This port is used to connect 9-pin serial mouse connector
and 25-pin serial port can be used to connect printer, scanner, and external
device. In serial communication data transfer rate is 1bit at a time with 115
Kbps speed.
a)
Parallel Ports/Printer Port:
25-pin Parallel Port:
This port can be used to
connect printer scanner and external device. In parallel communication data
transfer rate is 1-byte at a time with 150 KBps speed.
1) Standard Single-Function Port:
a)
The Keyboard Port:
Key Board Port –
-
5 Pin DIN
Connector
-
6 Pin PS/2 Port
b)
The Mouse Port:
-
9-pin Serial Port: (Now a day’s not in use)
-
PS2/Port – Used to connect PS/2 mouse.
c)
Video Port:
Video port can be used to connect video device like
monitor, projector, etc. Basically there are two types of Video Port:
i)
VGA (Video Graphics Adaptor):- VGA port present in
15-pin with three rows. In this port, we can connect, LCD (Liquid Crystal
Display) and CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) Monitor.
ii)
DVI (Digital Video Interface):- In this port only LCD
Monitor is connected in previous time.
d)
Audio Port:
Audio Port is used to connect audio device like speaker, microphone and
headphone.
i)
Green Color-
Speaker
ii)
Blue Color-
Headphone
iii)
Pink Color-
Microphone
e)
Multimedia Port:
This types of port can be support both audio and video
like TV card. This types of ports can be used HDMI (Higher Definition
Multimedia Interface) Connector.
f)
Joystick Port/Game Port: Game Port present in 15-pin
that can be used to connect joystick.
g)
Modem Port: This Port can be defined as network poet
who can be used for dial-up internet through a telephone line. This port uses
RJ11 Connector.
h)
Network
Interface Port:
This port is also other types of Network
Port, which can use cable internet and local area Network. This port can be
used RJ45 connector. (RJ- Registered Jack)
1)
Modern Multifunction Port:
a) USB (Universal Serial Bus):
It is the modern types of port which can
support 127 devices. Basically there are two types of USB, they are:
i) USB 1.1:- 12 mbps (speed)
ii) USB 2.0:- 480 mbps (speed)
It have two types of connector, they are:
(1) Type A Connector: - A connector which can be connected
in your computer.
(2) Type B Connector: - A connector which can be connected
in devices.
b) IEEE 1394 (Institute Of Electrical And Electrical
Engineers):
It is also other types of modern port, which
support different 63 devices. This port is also called as FireWire port (Apple)
or iLink, (Sony)
Basically there are two types of ports;
(1) IEEE 1394a- 400 mbps
(2) IEEE 1394b- 800 mbps
c) SCSI (Small Computer System Interface)
Units used in Computer
|
Mother Board
1.
AT Mother Board (AT-Advanced Technology)
-
Small than ATX
Motherboard.
-
5-Pin DIN for key
board connector.
-
Power supply
connector from SMPS to Mother Board is of 12 Pin.
2.
Baby AT
-
It has5-pin DIN
port for keyboard
-
It has 12-pin and
20-pin connector for SMPS
3.
ATX Mother Board (ATX – Advanced Technology Extended)
-
PS/2 key board
connector.
-
Power supply
connector from SMPS to Motherboard is of 20-Pin or 24-pin.
-
All most all
parts are built in.
34 Pin Connector
34-pin connector can be used to
connect Floppy Disk drive. Through a single 34-pin connector, we can connect 2 floppy
disk drive, when we can connect floppy disk drive, that time we can use 34-pin
data cable. (Flat Ribbon Cable)
40 Pin
Connector
On Motherboard there are two 40-oin connector, which
is present for Hard disk, CD-ROM, DVD-ROM & DVD-RW. Through a single 40-pin
connector, we can connect two devices. When, we connect that device into the
motherboard, that time we can use data cable (PATA Cable)
RAM Slots
It is used to fixed RAM cards. Basically there are
three types of RAM slots.
i.
SIMM Slot
ii.
DIMM slot
iii.
RIMM slot
1)
SIMM (Single Inline Memory Modules)
· SIMM are mostly in white color.
· RAM's which connect SIMM slots are connected in a 45°
angle.
· They come in 2 varieties:
i) 72 pins – capacity
1MB – 64MB
ii) 30 pins –
capacity 1MB – 16MB
· EDO RAM can use 72 pin SIMM slots and this slot is not
used any more.
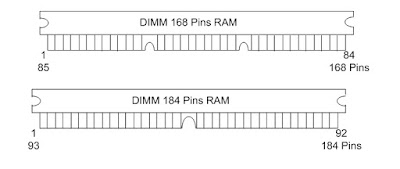
2) DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Modules)
· All latest computer use DIMM slots.
· They have white dips which help to lock the RAM into
place and they come in 2 varieties.
i.
168-pins –
capacity up to 512MB
ii.
184-pins –
capacity up to 1 GB
iii.
240-pins –
capacity up to 2 GB
· SDRAM uses 168-pins, DDR I uses 184-pins and DDR II
uses 240-pins DIMMs slots.
MICRO DIMM: It comes in 144 pins for LAPTOP computers.
SO DIMM
(Small outline DIMM): It comes in 72 pins and 144 pins for LAPTOP computers.
NOTE: - MICRO
DIMM & SO DIMM supports SDRAM & DDR SDRAM.
3) RIMM (Ram Bus Inline Memory Modules)
· RAM's which connect to RIMM slots have special heat
spreader on them for cooling.
· It comes in 184 pins and only supports RD RAM.
CPU Socket / ZIF Socket (ZIF – Zero
Insertion Force)
CPU socket on motherboard is used to mount
central processing unit this select is also called ZIF. A ZIF socket contains a
number on it which is asked to identify motherboard easily. According to CPU
socket number, we have to find out the type of Mother Board.
Socket 4, 5, 7 –
Pentium I
Socket 8 - Pentium Pro
Slot 1 - Pentium II
PGA 370 - Pentium III
PGA423 & PGA478 and LGA 775 - Pentium
IV and Core Processor
PGA418 & PGA611 - Itanium
(PGA-
Pin Grid Array and LGA- Land Grid Array)
Expansion BUS (slots)
Expansion
BUS
Expansion BUS is uses to extend the capability of
computer through expansion BUS or expansion slots. To these expansion buses
slots are connected these slots called as expansion slots.
Types
of Expansion BUS
1)
Internal
Expansion BUS slot
2)
External
Expansion BUS slot
1)
Internal
Expansion BUS slot :-
PCI (Peripheral Computer Inter
Connect)
Peripheral devices that plug in to the
PCI bus include Video Adapters, Sound Card, Net Work Interface Cards, Modem,
I/O Cards that add additional ports like parallel, serial or USB ports and
specialized devices such as Video Capture Card, TV tuner cards and SCSI
Adapter.
Although PCI slots are on the cutting
edge of PC technology, it is still going strong due to its strength, universal
adoption by computer markers and due to flexibility.
PCI sets between the front side BUS
and any other expansion BUS. This means that the PCI BUS, along with any
devices attached to it, easy able to work independently or with any other
expansion BUS.
PCI BUS works at the speed of 33 MHz
and 66 MHz At the speed of 33 MHz we can fixed device that run at 32 bit at the
speed of 66 MHz We can fixed the device which can run at 64 bit.
Self Configuration of PCI Slots
PCI works with plug and play device
and operating system to enable self configuration of system resources. (ID
address, IRQ and DMA channels)
The internal expansion slots are:-
i.
PCI: - This slot
looks like small and white colored, which is present for almost all types of
card, like TV Card, Modem Card, Sound Card, Network Card etc.
ii.
AGP: - This slot
found in brown colored, which is present for, VGA Card and 3D Games Cards. It
is bigger than CNR and AMR Slot.
iii.
CNR: - This slot
found in brown colored, which is present for Network card and Modem Card. It is
bigger than AMR slot.
iv.
AMR: - It is also
found in brown colored, which is present for Modem and Audio card.
v.
ISA: - This is
the old type of slot, which is found in large and black colored. This slot can
be used to connect all types of card in earlier time.
2) External Expansion BUS slot :-
a)
USB (Universal
Serial BUS)
b)
IEEE 1394
Power Connections from SMPS to
Devices
The PC’s Power supply converts high-voltage
alternating current (AC), Power into the lower Voltage Direct Current (DC)
Power that your motherboard and drives needs its internal fan also provides
essential cooling for the PC components and drives. In United States, standard
AC comes in somewhere between 110 and 120 volts, often written as ~115 V AC. Most of the rest of the world uses 220-240v
AC, So, many power supplies have a little switch in the back so you can use
them anywhere.
AT SMPS
-
Has 6+6=12 pin
connector from SMPS to Mother board.
-
The power supply
connector having written P8 & P9.
-
While connecting
P8 & P9 connector from SMPS to mother board Black colors wire of P8 &
P9 connector's co-inside each other.
ATX SMPS
Comes with 20-Pin or 24-Pin single
connector, i.e. P1 connector from SMPS to mother Board.
Connection From Mother Board to Hard
Disk
Connection From Mother Board to
CD-ROM or CD-R/W Drive
Molex Connector
Power Supply connector, used to connect from SMPS to
HD is called as Molex Connector.
Mini
Connector
Power
Supply connector, used to connect from SMPS to Floppy Disk is called as Mini
Connector.
CPU Technology
ALU
(Arithmetic Logical Unit):-
ALU
is the part of CPU that actually process data. An ALU takes data from the CPU
register, process it, and copes it back into the register before moving on to
the next batch of data.
FPU
(Floating Point Unit):-
FPU is the CPU component that handles
calculation based on floating point. The floating point unit is specialized CPU
component that processes graphic program & 3D game
Registers:-
Register are memory circuit locate inside
this CPU that hold data before & after processing. Early Intel processors
used primary 32- bit register and modern CPU use 64 & 128 bit register
size.
Clock Speed
The CPU
clock speed is a measurement of how many calculations a CPU execute per second.
1 calculation/second = 1Hz (Z = Hertz), billions of calculation per second call
MHz (Mega Hertz) but latest CPU measure in billions of cycle per second or
GHz(Giga Hertz).
The maximum
CPU speed is determined by two things. The speed of CPU itself and the maximum
speed of that motherboard is capable of handling. The CPU speed is determined
by manufacture & is set at the factory. The motherboard speed is determined
by onboard component called system crystal which is simply quartz crystal
circuit that oscillate
at a fix frequency when fed currents.
Cache Memory:
To add communication between the CPU &
RAM, the special type of memory called static RAM is used this is a cache
memory. Cache memory holds frequently using address location of RAM & data.
L1 –
Level One Cache Memory
L2 –
Level Two Cache Memory.
Basically there are two types
of cache memory.
1.
level 1 cache
------- built into CPU (internal cache memory)
2.
level 2 cache
------- present on motherboard (external cache memory)
Some Intel processors like Intel xenon & itanium
supports L3 cache memory
Clock Multiplayers
-
clock multiplayer
are the mechanism the CPU use to run at an even faster speed then set the
system crystal clocks.
-
All modern CPU
use the clocks multiplayer so in reality, any CPU as two speed. One is Internal
speed(it is actual speed of CPU & the external speed which is after clock
multiplication)
North Bridge Chip
The
north bridge chip is special (IC) controller circuit mounted on the motherboard
that assists the CPU. The North Bridge Chip connects the CPU to system RAM
Front Side Bus
The front side Bus is the collective term for the
physical pathways connecting the CPU, North Bridge Chip, & RAM. The front
side bus consists of two parts one is data bus & another is address bus. Data
Bus is pathway CPU access data in RAM. Address bus is a pathways that CPU uses
to talks with the other devices & to access the memory location of the RAM.
Address space:
-
RAM is made up of
millions of individuals storage circuits, similar to the cells of spread sheet
table. Each stores one bit of data. CPU read data 1 byte at a time so it takes
& individual cells to equal one addressable block of memory.
-
The numbers of
wires on the Address Bus defines the max amount of RAM. A CPU can addresses
this is called the ‘Address Space’.
64-bit Processor
A 64-bit CPU has general purpose, floating point unit and
address registers that are 64-bit wide, meaning they, can handled 64-bit wide
code in one pass-twice as wide as a 32-bit processor and they can address much
more memory. Both AMD and Intel currently produce 64-bit CPUs.
Multicore CPU
CPU clock speeds hit a practical limit of roughly 4GHz around
the years 2002-2003, motivating the CPU makers to find new ways to get more processing
power for CPU’s. Although Intel & AMD had different opinions about 64-bit
CPU’s both decided at Virtually the same time to combine two CPU’s into a
single chip; creating a dual-core Architecture. Dual Core isn’t just two CPU
has two execution units-two sets of pipeline but the two sets of pipeline share
caches and RAM. Both AMD and Intel also produce multicore. CPU’s of four or
eight cores on a Single Chip.
Pentium
Intel
popular processor line as now was around for over 10 years. Intel Pentium has
64 bit data bus & 32 bit address bus. Pentium processor consumes 5 volts.
Later version ran at more modem standard of 3.3 volts.
-
P4 processor
supports 4 GB RAM